Poll Will Not Let the Rest of the Program Continue Python

Introduction to Python User Input
While programming very often, we are required to take input from the user so as to manipulate the data and process it thereafter. This ensures the program's dynamism and robustness as it is not hardcoded and can successfully execute at any random value given by the user. In this topic, we are going to learn about Python User Input.
In today's article, we would learn about the concept of accepting input from the user at the run time of the program for Python programming language and process that data. This ensures proper communication between the program and the outside world.
Methods of Inputting Data
The following are the ways of inputting data from the user: –
- input()
- raw_input()
Both basically do the same task, the only difference being the version of Python, which supports the two functions.
raw_input was used in older versions of Python, and it got replaced by input() in recent Python versions.
In this article, we would discuss input() as it is used in recent versions of Python.
Working of Python Input()
When we use the input() function in our program, the flow of execution is halted till the user inputs the data and clicks the Enter button. After that, the user's value input is stored in some variable in the form of a string. No matter what data type the user intended their data to be, it gets stored as a string only. It needs to explicitly typecast to the desired format before use. Later we will look at such an example where if we do not typecast the data, it will result in an error.
Now let us have a look at the syntax of input()
Syntax
input([<prompt from user>]) Now let us see some examples and discuss how to use input() to accept data from users for different scenarios.
Examples of Python User Input
Here are the following examples mention below:
Example #1
Inputting normal text from the keyboard
Code:
string1 = input() print(string1) Output
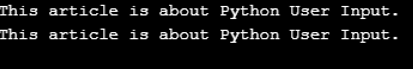
Explanation
In the first line, we used the input() function to take input from the user and store it in the variable named string1. After we press the Enter button, we are instructed to provide our input by the show of a blank input box with a cursor blinking. When we provide the input and press the Enter button, then that value gets stored in the variable named string1. In the next line, when we are printing the variable, we actually see that the input provided by us is actually printed in the console.
Example #2
Inputting number from the console and finding its square
Code:
print("Enter number to find the square:") number = input() print("The Square of number {}".format(number,number**2)) Output
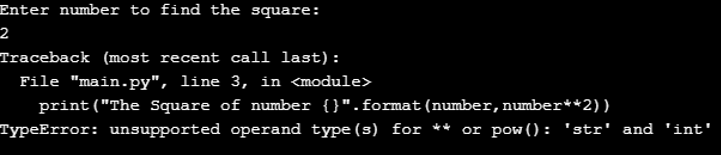
Explanation
Here we encounter a TypeError, and if we read the errorMessage, it suggests to us that the first argument, i.e. number variable string datatype. And because of that, it is not able to perform the power operation on that. It is important to note here that the input data type is always taken as a string, so it must be typecast to the desired datatype before it can be worked on.
Let us correct the code and have a look at the output.
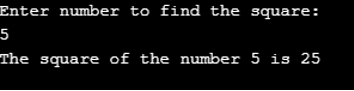
Code
print("Enter number to find the square:") number = input() number = int(number) print("The square of the number {} is {}".format(number,number**2)) Output
Example #3
Inputting multiple numbers and finding out the maximum from them
Code:
import numpy as np print("How many numbers we want to find the maximum of:") n=int(input()) numbers = [] for i in range(0, n): ele = int(input("Enter elements: ")) numbers.append(ele) print("The Maximum Number is:", max(numbers)) Output
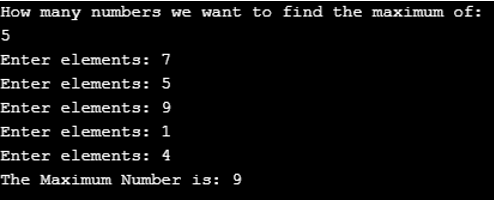
Example #4
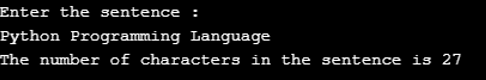
Inputting sentence and counting the number of characters in that
Code:
print("Enter the sentence :") sentence = input() length = len(sentence) print("The number of characters in the sentence is {}".format(length)) Output
Conclusion
Finally, it is time to draw closure to this article. In today's article, we learned about the input() function of Python. We looked at the syntax and discussed different examples and use cases. So next time you write a Python program, do remember to use the concepts of input() and test your program on many random user input data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python User Input. Here we discuss the methods, working, and the examples of Python User Input along with the appropriate syntax. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- Python yield
- Python Switch Case
- Python Slice String
- Python Constants
Source: https://www.educba.com/python-user-input/
0 Response to "Poll Will Not Let the Rest of the Program Continue Python"
Post a Comment